PINNs: Oscillator analysis#
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import base64
from IPython.display import HTML, display
import imageio
from tqdm import tqdm
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
# Ensure reproducibility
torch.manual_seed(0)
np.random.seed(0)
class HarmonicOscillator:
def __init__(self, damping_coefficient, natural_frequency):
self.d = damping_coefficient
self.w0 = natural_frequency
assert self.d < self.w0, "Damping coefficient must be less than natural frequency for underdamped oscillator"
self.w = np.sqrt(self.w0**2 - self.d**2)
self.phi = np.arctan(-self.d / self.w)
self.A = 1 / (2 * np.cos(self.phi))
def analytical_solution(self, t):
"""Analytical solution to the 1D underdamped harmonic oscillator problem."""
cos_part = np.cos(self.phi + self.w * t)
exp_part = np.exp(-self.d * t)
u = exp_part * 2 * self.A * cos_part
return u
def analytical_derivative(self, t):
"""Analytical derivative of the solution."""
du_dt = -self.d * self.analytical_solution(t) - 2 * self.A * self.w * np.sin(self.phi + self.w * t) * np.exp(-self.d * t)
return du_dt
def generate_data(self):
"""Generates training data for the oscillator."""
t = np.linspace(0, 1, 500).reshape(-1, 1)
u = self.analytical_solution(t).reshape(-1, 1)
t_data = t[0:200:20]
u_data = u[0:200:20]
return t, u, t_data, u_data
class Visualizer:
def __init__(self):
# Remove seaborn style to have more control over the plot appearance
plt.style.use('default')
def plot_result(self, t, u_exact, t_data, u_data, u_pred, t_physics=None, iteration=None, title=""):
"""
Plots the results with improved visualization.
Args:
t: time array for the full solution
u_exact: exact displacement solution
t_data: time array of training data points
u_data: displacement data of training data points
u_pred: predicted displacement from the neural network
t_physics: optional physics points for PINN visualization
iteration: optional iteration number for animation
title: optional title for the plot
Returns:
image: numpy array containing the plot image
"""
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
# Remove grid but keep the box
ax.grid(False)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(True)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(True)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_visible(True)
ax.spines['left'].set_visible(True)
# Plot exact solution
ax.plot(t, u_exact, color="gray", linewidth=2, linestyle='--', label="Exact Solution")
# Plot neural network prediction
ax.plot(t, u_pred, color="blue", linewidth=2, label="Neural Network Prediction")
# Plot training data points
ax.scatter(t_data, u_data, color="red", s=50, label="Training Data")
# Plot physics points if provided (for PINN)
if t_physics is not None:
ax.scatter(t_physics, np.zeros_like(t_physics), color="green", s=50, label="Physics Points", marker="^")
# Add iteration number if provided
if iteration is not None:
ax.set_title(f"Training Step: {iteration+1} {title}")
ax.legend(frameon=True, facecolor='white', edgecolor='black')
ax.set_xlabel("Time (t)")
ax.set_ylabel("Displacement u(t)")
ax.set_xlim([t.min(), t.max()])
ax.set_ylim([-1.2, 1.2])
# Set background color to white
ax.set_facecolor('white')
fig.patch.set_facecolor('white')
# Convert plot to image array
fig.canvas.draw()
image = np.frombuffer(fig.canvas.buffer_rgba(), dtype='uint8')
image = image.reshape(fig.canvas.get_width_height()[::-1] + (4,))
plt.close(fig)
return image
def create_animation(self, frames, filename='animation.gif', fps=5):
"""Creates and saves an animation from frames."""
imageio.mimsave(filename, frames, fps=fps)
def display_animation(self, filename='animation.gif'):
"""Displays the animation as HTML."""
with open(filename, 'rb') as f:
data = f.read()
data_url = "data:image/gif;base64," + base64.b64encode(data).decode()
display(HTML('<img src="{}">'.format(data_url)))
class NeuralNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layer_sizes):
super(NeuralNetwork, self).__init__()
layers = []
for in_size, out_size in zip(layer_sizes[:-1], layer_sizes[1:]):
layers.append(nn.Linear(in_size, out_size))
layers.append(nn.Tanh())
layers.pop() # Remove the last activation function
self.model = nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
return self.model(x)
def pinn_loss(model, t_data, u_data, t_physics, mu, k):
"""Computes the loss for PINN, including data and physics losses."""
# Data loss
u_pred = model(t_data)
loss_data = nn.MSELoss()(u_pred, u_data)
# Physics loss
t_physics = t_physics.clone().detach().requires_grad_(True)
u_physics = model(t_physics)
du_dt = torch.autograd.grad(u_physics, t_physics, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(u_physics),
create_graph=True)[0]
d2u_dt2 = torch.autograd.grad(du_dt, t_physics, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(du_dt),
create_graph=True)[0]
physics = d2u_dt2 + mu * du_dt + k * u_physics
loss_physics = 1e-4 * torch.mean(physics ** 2)
return loss_data + loss_physics
def train_standard_nn(ho, visualizer, layer_sizes, num_steps=1000, record_interval=100):
"""Trains a standard neural network and collects parameter trajectories."""
t, u_exact, t_data, u_data = ho.generate_data()
# Initialize neural network model
model = NeuralNetwork(layer_sizes)
model.train()
# Prepare data
t_data_tensor = torch.tensor(t_data, dtype=torch.float32)
u_data_tensor = torch.tensor(u_data, dtype=torch.float32)
t_full_tensor = torch.tensor(t, dtype=torch.float32)
# Define optimizer and loss function
learning_rate = 1e-3
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
# Training loop
frames = []
losses = []
param_trajectory = []
for step in tqdm(range(num_steps), desc="Training Standard NN"):
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
u_pred = model(t_data_tensor)
loss = criterion(u_pred, u_data_tensor)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
losses.append(loss.item())
# Store parameter vector
param_vector = []
for param in model.parameters():
param_vector.append(param.data.cpu().numpy().flatten())
param_vector = np.concatenate(param_vector)
param_trajectory.append(param_vector)
# Record frames for animation
if (step + 1) % record_interval == 0:
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
u_pred_full = model(t_full_tensor).numpy()
image = visualizer.plot_result(t, u_exact, t_data, u_data, u_pred_full, iteration=step, title="[Standard NN]")
frames.append(image)
# Create and display animation
visualizer.create_animation(frames, filename='oscillator_nn.gif', fps=2)
visualizer.display_animation('oscillator_nn.gif')
return model, losses, np.array(param_trajectory)
def train_pinn(ho, visualizer, layer_sizes, num_steps=20000, record_interval=1500):
"""Trains a physics-informed neural network and collects parameter trajectories."""
t, u_exact, t_data, u_data = ho.generate_data()
# Physics points for PINN
t_physics = np.linspace(0, 1, 30).reshape(-1, 1)
mu = 2 * ho.d
k_param = ho.w0**2
# Initialize neural network model
model = NeuralNetwork(layer_sizes)
model.train()
# Prepare data
t_data_tensor = torch.tensor(t_data, dtype=torch.float32)
u_data_tensor = torch.tensor(u_data, dtype=torch.float32)
t_full_tensor = torch.tensor(t, dtype=torch.float32)
t_physics_tensor = torch.tensor(t_physics, dtype=torch.float32)
mu_tensor = torch.tensor(mu, dtype=torch.float32)
k_param_tensor = torch.tensor(k_param, dtype=torch.float32)
# Define optimizer
learning_rate = 1e-4
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# Training loop
frames = []
losses = []
param_trajectory = []
for step in tqdm(range(num_steps), desc="Training PINN"):
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = pinn_loss(model, t_data_tensor, u_data_tensor, t_physics_tensor, mu_tensor, k_param_tensor)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
losses.append(loss.item())
# Store parameter vector
param_vector = []
for param in model.parameters():
param_vector.append(param.data.cpu().numpy().flatten())
param_vector = np.concatenate(param_vector)
param_trajectory.append(param_vector)
# Record frames for animation
if (step + 1) % record_interval == 0:
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
u_pred_full = model(t_full_tensor).numpy()
image = visualizer.plot_result(t, u_exact, t_data, u_data, u_pred_full,
t_physics=t_physics, iteration=step, title="[PINN]")
frames.append(image)
# Create and display animation
visualizer.create_animation(frames, filename='oscillator_pinn.gif', fps=2)
visualizer.display_animation('oscillator_pinn.gif')
return model, losses, np.array(param_trajectory)
def evaluate_lipschitz_constant(model, t_samples):
"""
Evaluates the Lipschitz constant of the model over the sampled t values.
Args:
model: Trained neural network model
t_samples: Numpy array of t values
Returns:
lipschitz_constant: Estimated Lipschitz constant
du_dt: Array of derivative values
"""
model.eval() # Set model to evaluation mode
# Enable gradient tracking
t_tensor = torch.tensor(t_samples, dtype=torch.float32, requires_grad=True).reshape(-1,1)
u_pred = model(t_tensor)
# Compute derivatives
du_dt = torch.autograd.grad(u_pred, t_tensor, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(u_pred),
create_graph=False)[0]
du_dt_np = du_dt.detach().numpy().flatten()
lipschitz_constant = np.max(np.abs(du_dt_np))
return lipschitz_constant, du_dt_np
def estimate_rademacher_complexity(model, t_samples, num_trials=100):
"""
Estimates the Rademacher complexity of a trained model.
Args:
model: Trained neural network model
t_samples: Numpy array of t values
num_trials: Number of random label assignments to average over
Returns:
rademacher_complexity: Estimated Rademacher complexity
"""
model.eval()
n = len(t_samples)
rademacher_sum = 0.0
with torch.no_grad():
t_tensor = torch.tensor(t_samples, dtype=torch.float32).reshape(-1,1)
u_pred = model(t_tensor).numpy().flatten()
for _ in tqdm(range(num_trials), desc="Estimating Rademacher Complexity"):
# Generate random Rademacher labels (+1 or -1)
sigma = np.random.choice([-1, 1], size=n)
# Compute the correlation
rademacher_sum += np.abs(np.dot(sigma, u_pred)) / n
rademacher_complexity = rademacher_sum / num_trials
return rademacher_complexity
def perform_pca(param_trajectory, n_components=2):
"""
Performs PCA on the parameter trajectory to find principal directions.
Args:
param_trajectory: Array of parameter vectors (num_steps x num_params)
n_components: Number of principal components to return
Returns:
components: Principal components (n_components x num_params)
pca_model: Fitted PCA model
"""
pca = PCA(n_components=n_components)
pca.fit(param_trajectory)
components = pca.components_
return components, pca
def evaluate_loss_landscape_pca(model, model_type, loss_function, pca_components, param_step=0.1, param_range=1.0):
"""
Evaluates the loss landscape around the current model parameters using PCA components.
Args:
model: Trained neural network model
model_type: 'standard' or 'pinn'
loss_function: Function to compute the loss
pca_components: Tuple of two principal components (numpy arrays)
param_step: Step size for parameter perturbation
param_range: Range for parameter perturbation
Returns:
X, Y, Z: Meshgrid arrays and corresponding loss values
"""
# Extract current model parameters as a single vector
original_params = []
for param in model.parameters():
original_params.append(param.data.cpu().numpy().flatten())
original_params = np.concatenate(original_params)
# Directions
d1, d2 = pca_components
# Create a grid
alpha = np.linspace(-param_range, param_range, 50)
beta = np.linspace(-param_range, param_range, 50)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(alpha, beta)
Z = np.zeros_like(X)
# Iterate over the grid and compute loss
for i in tqdm(range(X.shape[0]), desc=f"Evaluating Loss Landscape [{model_type}]"):
for j in range(X.shape[1]):
# Perturb parameters
perturbed_params = original_params + X[i, j] * d1 + Y[i, j] * d2
# Load perturbed parameters into the model
current_idx = 0
for param in model.parameters():
param_shape = param.data.cpu().numpy().shape
param_size = param.data.numel()
new_values = perturbed_params[current_idx:current_idx + param_size]
new_values = new_values.reshape(param_shape)
param.data = torch.tensor(new_values, dtype=torch.float32)
current_idx += param_size
# Compute loss
loss = loss_function(model).item()
Z[i, j] = loss
# Restore original parameters
current_idx = 0
for param in model.parameters():
param_shape = param.data.cpu().numpy().shape
param_size = param.data.numel()
original_values = original_params[current_idx:current_idx + param_size]
original_values = original_values.reshape(param_shape)
param.data = torch.tensor(original_values, dtype=torch.float32)
current_idx += param_size
return X, Y, Z
def standard_loss(model, ho):
"""Loss function for standard NN: MSE on data."""
t, u_exact, t_data, u_data = ho.generate_data()
t_data_tensor = torch.tensor(t_data, dtype=torch.float32)
u_data_tensor = torch.tensor(u_data, dtype=torch.float32)
u_pred = model(t_data_tensor)
return nn.MSELoss()(u_pred, u_data_tensor)
def pinn_total_loss(model, ho):
"""Total loss function for PINN: data + physics."""
t, u_exact, t_data, u_data = ho.generate_data()
t_physics = np.linspace(0, 1, 30).reshape(-1, 1)
mu = 2 * ho.d
k_param = ho.w0**2
# Prepare tensors
t_data_tensor = torch.tensor(t_data, dtype=torch.float32)
u_data_tensor = torch.tensor(u_data, dtype=torch.float32)
t_physics_tensor = torch.tensor(t_physics, dtype=torch.float32)
mu_tensor = torch.tensor(mu, dtype=torch.float32)
k_param_tensor = torch.tensor(k_param, dtype=torch.float32)
return pinn_loss(model, t_data_tensor, u_data_tensor, t_physics_tensor, mu_tensor, k_param_tensor)
def main():
# Initialize harmonic oscillator with underdamped parameters
ho = HarmonicOscillator(damping_coefficient=2, natural_frequency=20)
# Initialize visualizer
visualizer = Visualizer()
# Define network sizes to evaluate
network_sizes = [8, 16, 32, 64, 128]
# Initialize lists to store Lipschitz constants and Rademacher complexities
lipschitz_standard = []
lipschitz_pinn = []
rademacher_standard = []
rademacher_pinn = []
# To determine consistent z-axis limits for loss landscapes
all_loss_values = []
# Initialize lists to store derivatives
derivatives_standard = []
derivatives_pinn = []
# Compute the exact Lipschitz constant
t_samples_exact = np.linspace(0, 1, 1000)
du_dt_exact = ho.analytical_derivative(t_samples_exact)
lip_exact = np.max(np.abs(du_dt_exact))
print(f"Exact Solution Lipschitz Constant: {lip_exact:.4f}")
for size in network_sizes:
print(f"\n=== Network Size: {size} ===")
# Define layer sizes based on current network size
layer_sizes = [1] + [size]*3 + [1]
# Train Standard NN
print("\n--- Training Standard Neural Network ---")
standard_model, standard_losses, standard_params = train_standard_nn(ho, visualizer, layer_sizes)
# Train PINN
print("\n--- Training Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN) ---")
pinn_model, pinn_losses, pinn_params = train_pinn(ho, visualizer, layer_sizes)
# Perform PCA on parameter trajectories
print("\n--- Performing PCA on Parameter Trajectories ---")
print("Standard NN:")
standard_components, standard_pca = perform_pca(standard_params)
print("PINN:")
pinn_components, pinn_pca = perform_pca(pinn_params)
# Define loss functions with access to harmonic oscillator
def standard_loss_fn(model):
return standard_loss(model, ho)
def pinn_loss_fn(model):
return pinn_total_loss(model, ho)
# Evaluate loss landscapes
print("\n--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for Standard NN ---")
X_std, Y_std, Z_std = evaluate_loss_landscape_pca(
standard_model,
model_type='Standard NN',
loss_function=standard_loss_fn,
pca_components=standard_components,
param_step=0.1,
param_range=1.0
)
print("\n--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for PINN ---")
X_pinn, Y_pinn, Z_pinn = evaluate_loss_landscape_pca(
pinn_model,
model_type='PINN',
loss_function=pinn_loss_fn,
pca_components=pinn_components,
param_step=0.1,
param_range=1.0
)
# Collect all loss values to determine global z-axis limit
all_loss_values.extend([Z_std.max(), Z_pinn.max()])
# Store loss landscapes for plotting later
if 'loss_landscapes_std' not in locals():
loss_landscapes_std = []
loss_landscapes_pinn = []
loss_landscapes_std.append((X_std, Y_std, Z_std))
loss_landscapes_pinn.append((X_pinn, Y_pinn, Z_pinn))
# Evaluate Lipschitz Constants
print("\n--- Evaluating Lipschitz Constants ---")
# Define a dense set of t samples
t_samples = np.linspace(0, 1, 1000)
# Standard NN
lip_std, du_dt_std = evaluate_lipschitz_constant(standard_model, t_samples)
print(f"Standard NN Lipschitz Constant: {lip_std:.4f}")
lipschitz_standard.append(lip_std)
derivatives_standard.append(du_dt_std)
# PINN
lip_pinn, du_dt_pinn = evaluate_lipschitz_constant(pinn_model, t_samples)
print(f"PINN Lipschitz Constant: {lip_pinn:.4f}")
lipschitz_pinn.append(lip_pinn)
derivatives_pinn.append(du_dt_pinn)
# Estimate Rademacher Complexity
print("\n--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for Standard NN ---")
rademacher_std = estimate_rademacher_complexity(standard_model, t_samples, num_trials=100)
print(f"Standard NN Rademacher Complexity: {rademacher_std:.4f}")
rademacher_standard.append(rademacher_std)
print("\n--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for PINN ---")
rademacher_pinn_value = estimate_rademacher_complexity(pinn_model, t_samples, num_trials=100)
print(f"PINN Rademacher Complexity: {rademacher_pinn_value:.4f}")
rademacher_pinn.append(rademacher_pinn_value)
# Determine global z-axis limit for loss landscapes
max_loss = max(all_loss_values) * 1.1 # Add 10% buffer
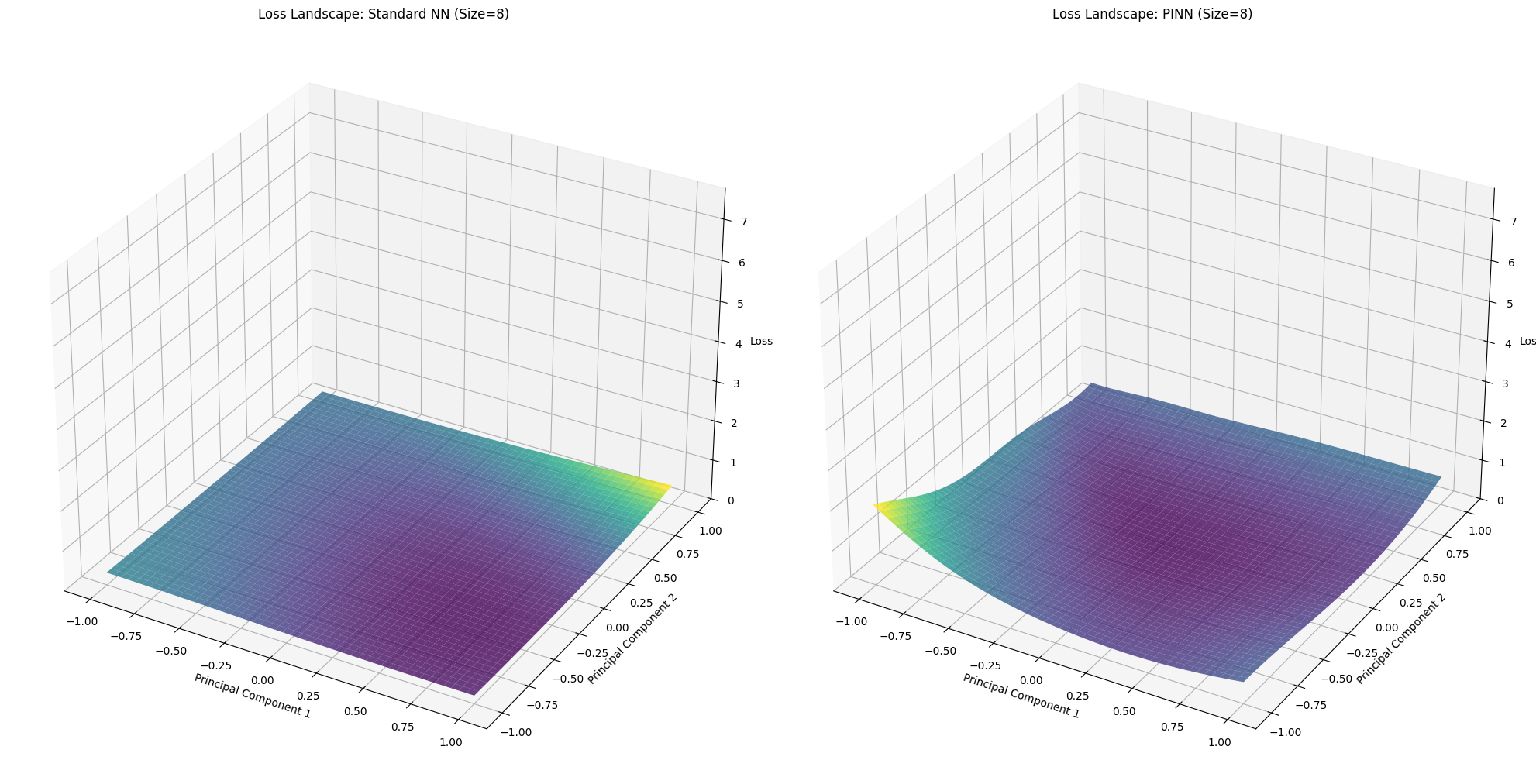
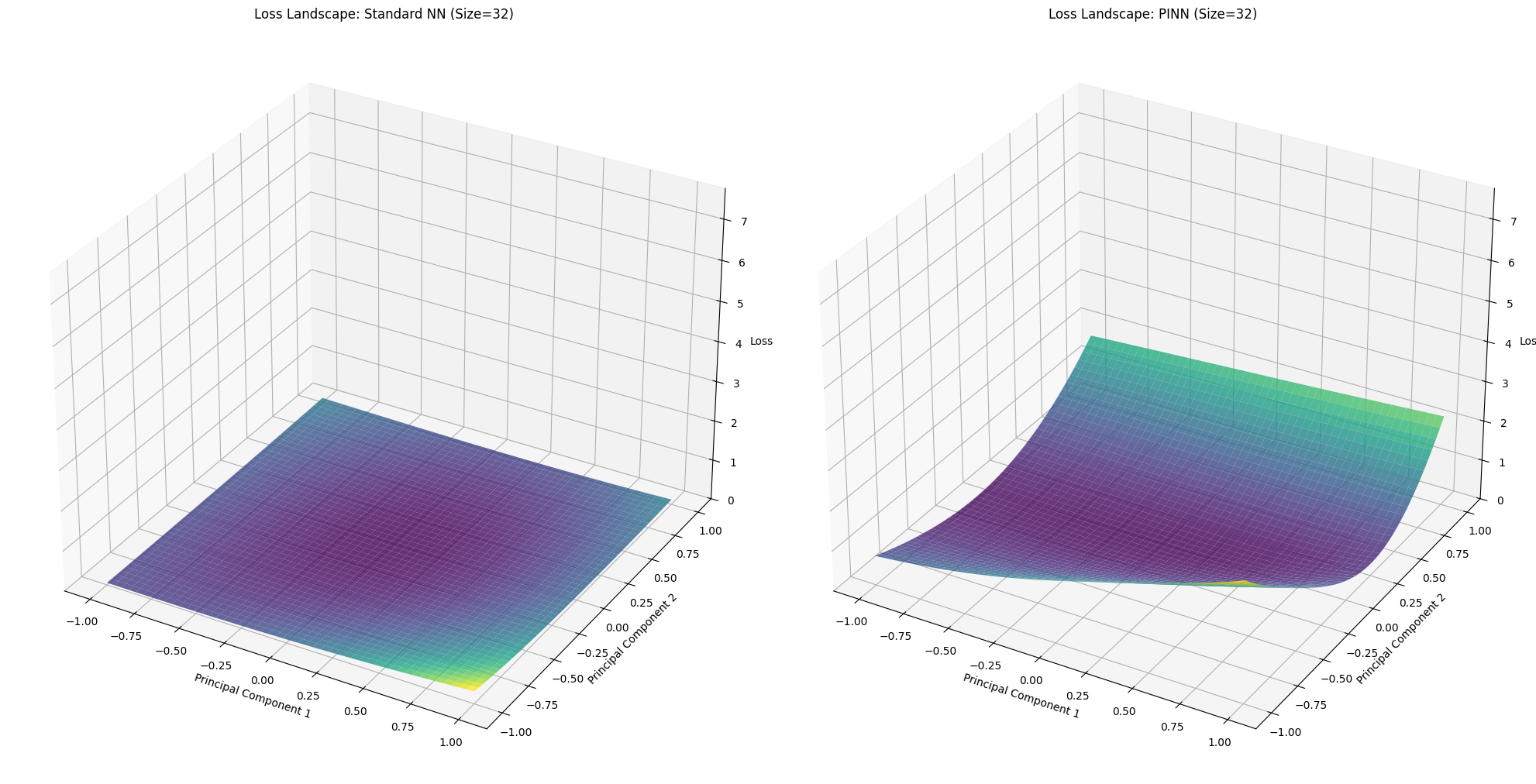
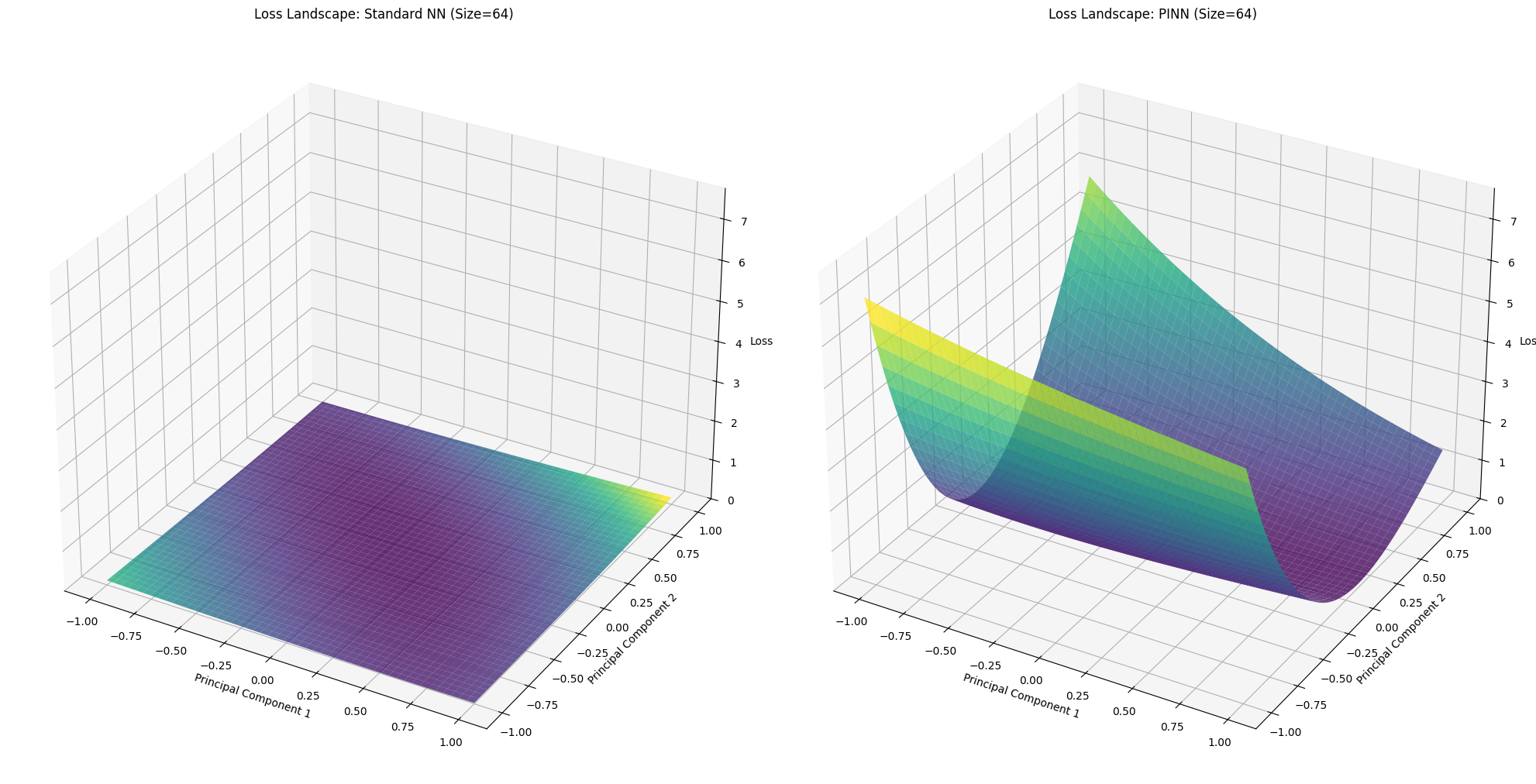
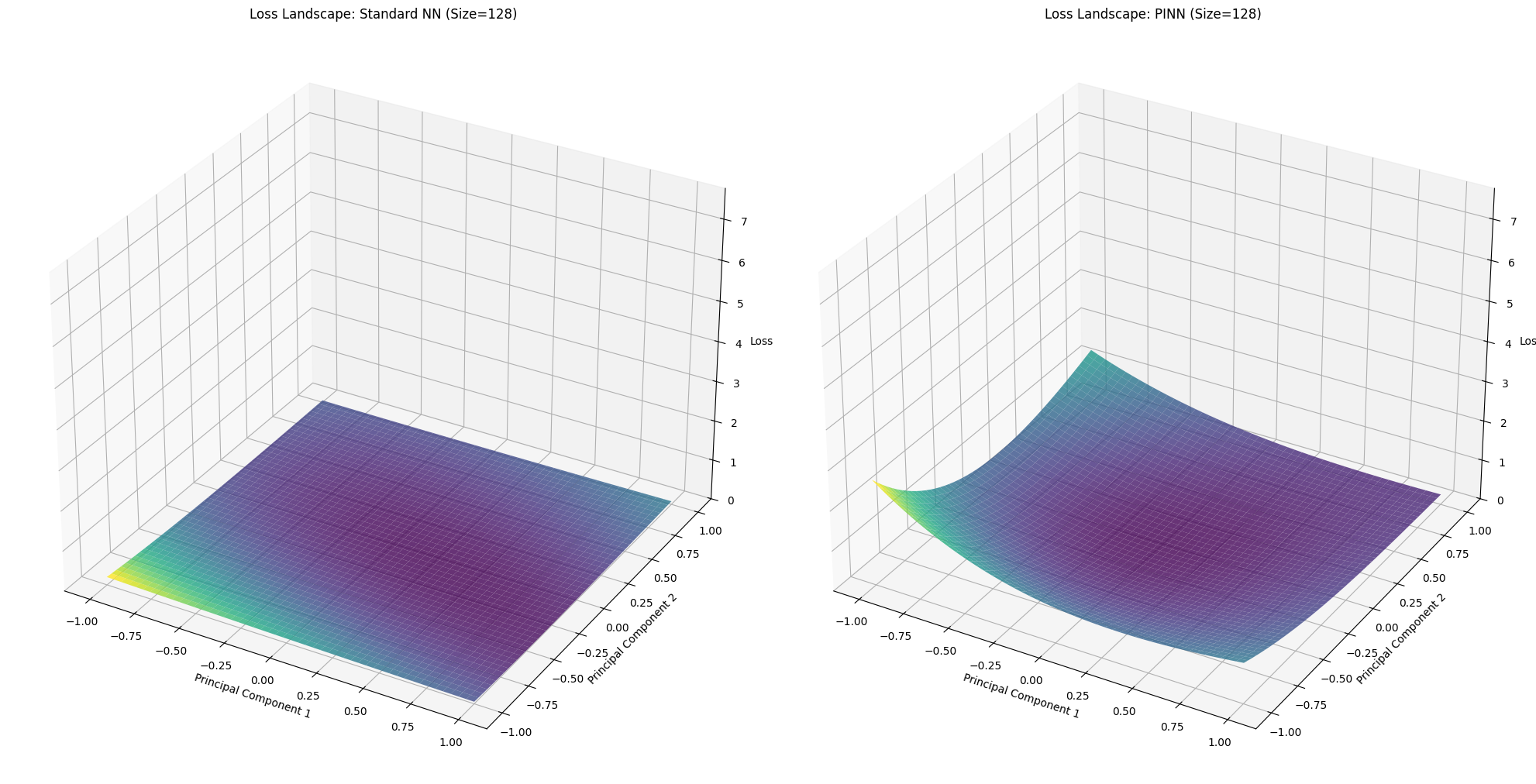
# Plot loss landscapes for all network sizes with the same z-axis scale
for idx, size in enumerate(network_sizes):
X_std, Y_std, Z_std = loss_landscapes_std[idx]
X_pinn, Y_pinn, Z_pinn = loss_landscapes_pinn[idx]
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
# Standard NN Loss Landscape
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1, projection='3d')
ax1.plot_surface(X_std, Y_std, Z_std, cmap='viridis', alpha=0.8)
ax1.set_title(f'Loss Landscape: Standard NN (Size={size})')
ax1.set_xlabel('Principal Component 1')
ax1.set_ylabel('Principal Component 2')
ax1.set_zlabel('Loss')
ax1.set_zlim(0, max_loss)
# PINN Loss Landscape
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2, projection='3d')
ax2.plot_surface(X_pinn, Y_pinn, Z_pinn, cmap='viridis', alpha=0.8)
ax2.set_title(f'Loss Landscape: PINN (Size={size})')
ax2.set_xlabel('Principal Component 1')
ax2.set_ylabel('Principal Component 2')
ax2.set_zlabel('Loss')
ax2.set_zlim(0, max_loss)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
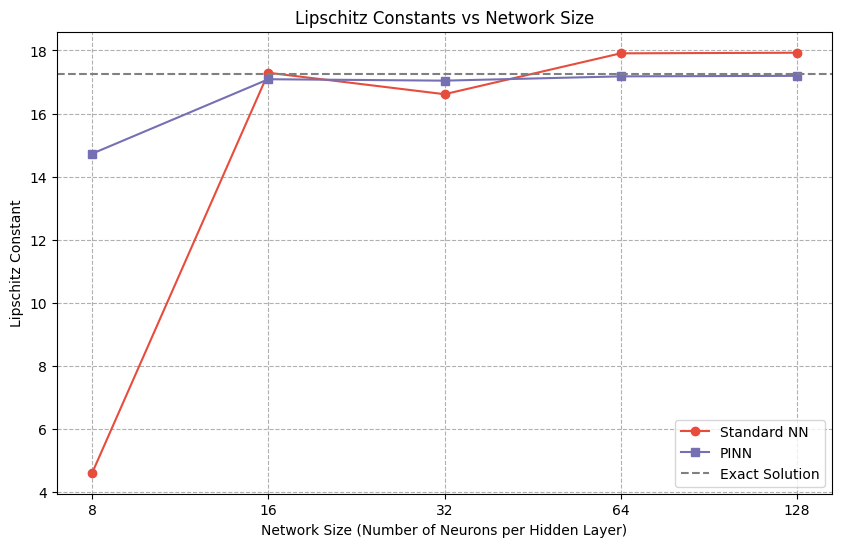
# Plot Lipschitz Constants vs Network Size
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(network_sizes, lipschitz_standard, marker='o', label='Standard NN', color='#E74C3C') # E74C3C
plt.plot(network_sizes, lipschitz_pinn, marker='s', label='PINN', color='#7570b3') # #7570b3
plt.axhline(y=lip_exact, color='gray', linestyle='--', label='Exact Solution')
plt.title('Lipschitz Constants vs Network Size')
plt.xlabel('Network Size (Number of Neurons per Hidden Layer)')
plt.ylabel('Lipschitz Constant')
plt.xscale('log', base=2) # Corrected keyword argument
plt.xticks(network_sizes, network_sizes)
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, which="both", ls="--")
plt.show()
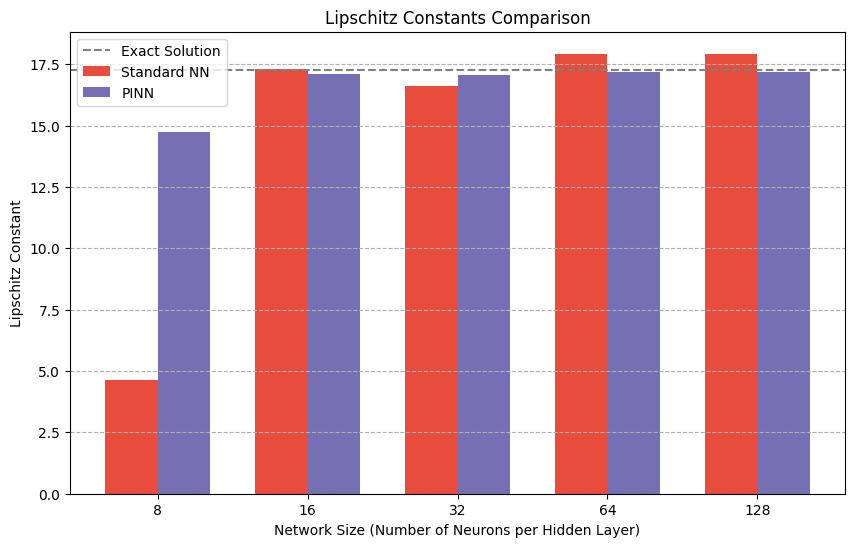
# Additionally, plot the Lipschitz constants as a bar chart
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
bar_width = 0.35
indices = np.arange(len(network_sizes))
plt.bar(indices - bar_width/2, lipschitz_standard, bar_width, label='Standard NN', color='#E74C3C') # E74C3C
plt.bar(indices + bar_width/2, lipschitz_pinn, bar_width, label='PINN', color='#7570b3') # #7570b3
# Plot exact Lipschitz constant as a horizontal line
plt.axhline(y=lip_exact, color='gray', linestyle='--', label='Exact Solution')
plt.title('Lipschitz Constants Comparison')
plt.xlabel('Network Size (Number of Neurons per Hidden Layer)')
plt.ylabel('Lipschitz Constant')
plt.xticks(indices, network_sizes)
plt.legend()
plt.grid(axis='y', linestyle='--')
plt.show()
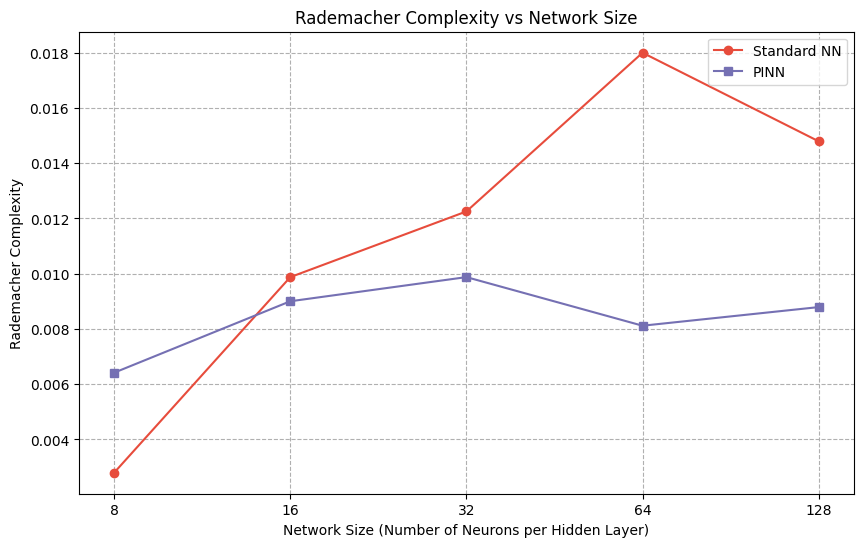
# Plot Rademacher Complexity vs Network Size
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(network_sizes, rademacher_standard, marker='o', label='Standard NN', color='#E74C3C') # E74C3C
plt.plot(network_sizes, rademacher_pinn, marker='s', label='PINN', color='#7570b3') # #7570b3
plt.title('Rademacher Complexity vs Network Size')
plt.xlabel('Network Size (Number of Neurons per Hidden Layer)')
plt.ylabel('Rademacher Complexity')
plt.xscale('log', base=2) # Logarithmic scale
plt.xticks(network_sizes, network_sizes)
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, which="both", ls="--")
plt.show()
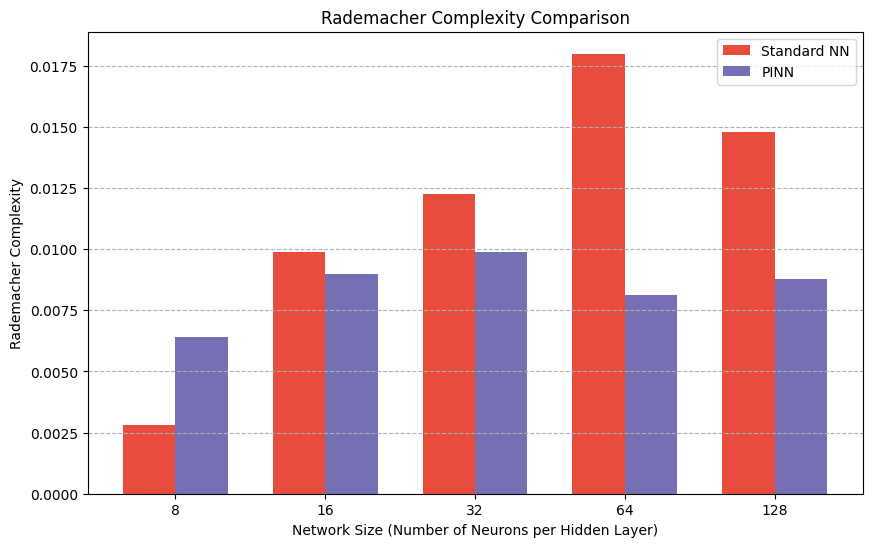
# Additionally, plot the Rademacher complexities as a bar chart
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
bar_width = 0.35
indices = np.arange(len(network_sizes))
plt.bar(indices - bar_width/2, rademacher_standard, bar_width, label='Standard NN', color='#E74C3C') # E74C3C
plt.bar(indices + bar_width/2, rademacher_pinn, bar_width, label='PINN', color='#7570b3') # #7570b3
plt.title('Rademacher Complexity Comparison')
plt.xlabel('Network Size (Number of Neurons per Hidden Layer)')
plt.ylabel('Rademacher Complexity')
plt.xticks(indices, network_sizes)
plt.legend()
plt.grid(axis='y', linestyle='--')
plt.show()
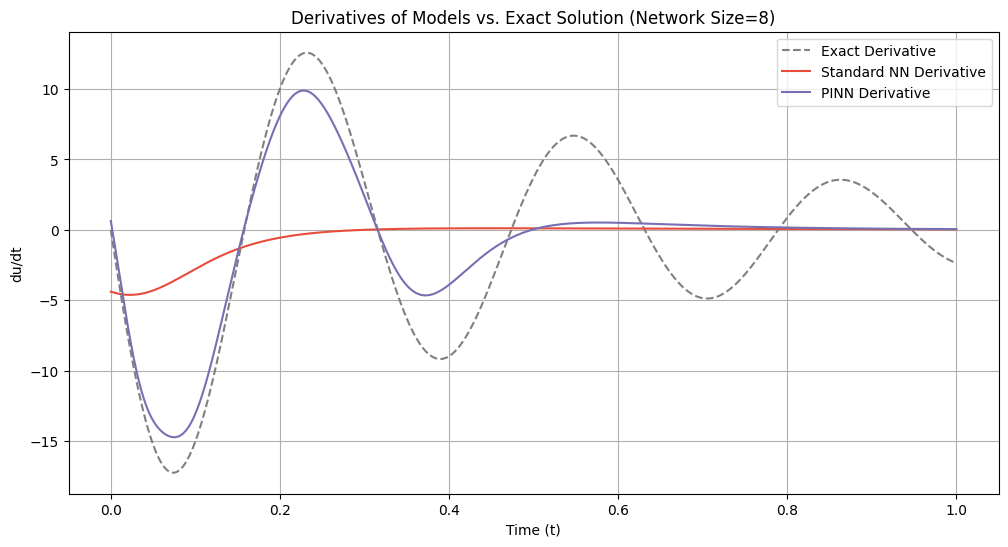
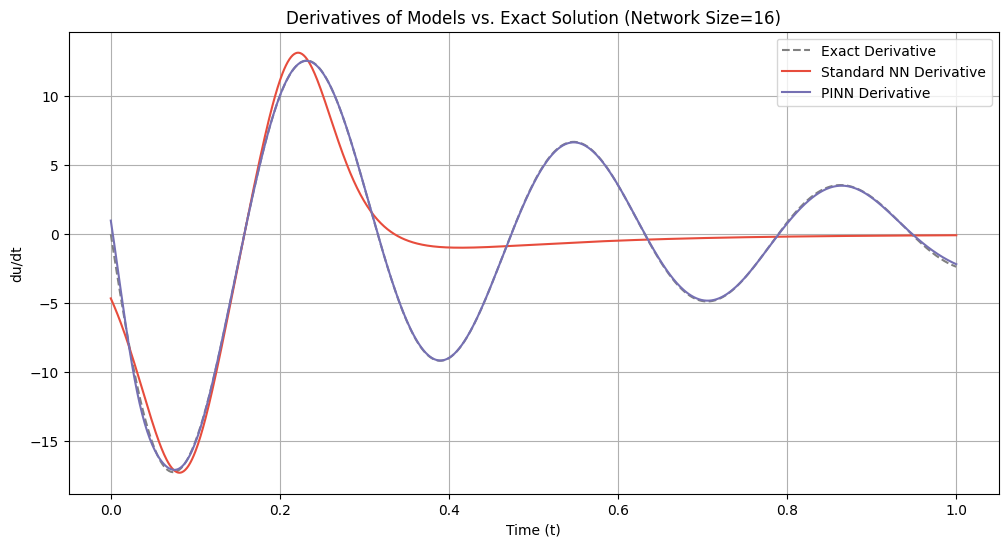
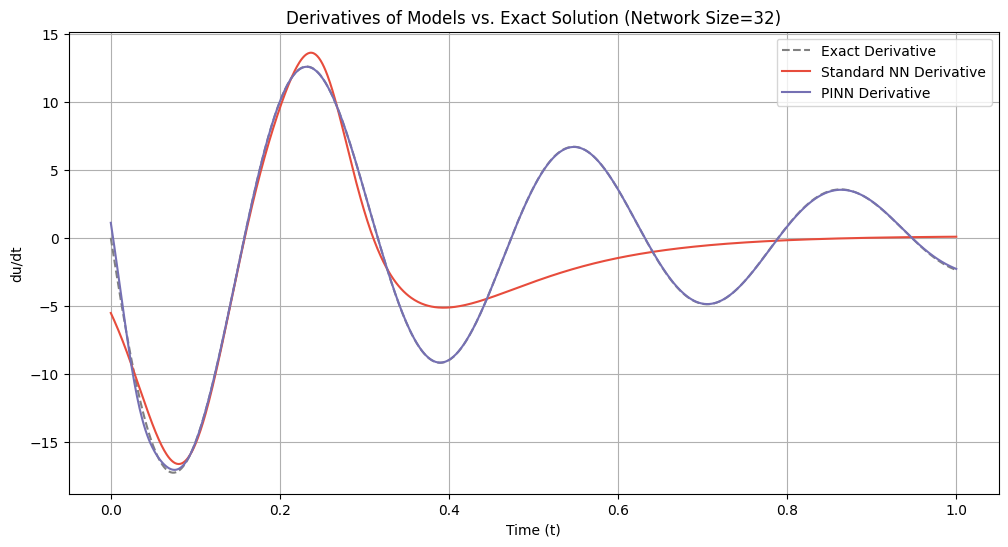
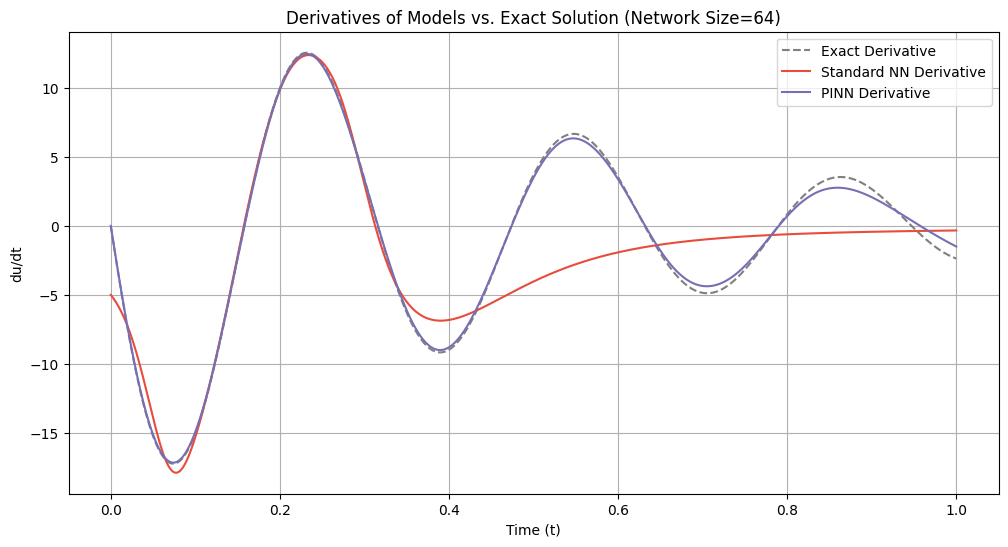
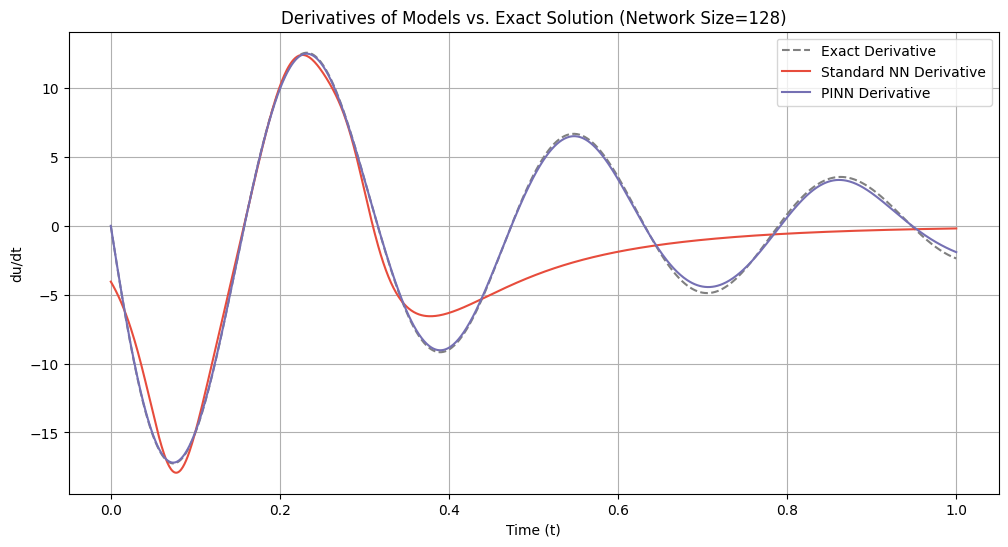
# Plot derivatives for each network size
for idx, size in enumerate(network_sizes):
du_dt_std = derivatives_standard[idx]
du_dt_pinn = derivatives_pinn[idx]
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(t_samples_exact, du_dt_exact, label='Exact Derivative', color='gray', linestyle='--')
plt.plot(t_samples_exact, du_dt_std, label='Standard NN Derivative', color='#E74C3C')
plt.plot(t_samples_exact, du_dt_pinn, label='PINN Derivative', color='#7570b3')
plt.title(f'Derivatives of Models vs. Exact Solution (Network Size={size})')
plt.xlabel('Time (t)')
plt.ylabel('du/dt')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Exact Solution Lipschitz Constant: 17.2519
=== Network Size: 8 ===
--- Training Standard Neural Network ---
Training Standard NN: 100%|██████████| 1000/1000 [00:00<00:00, 2184.10it/s]
--- Training Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN) ---
Training PINN: 100%|██████████| 20000/20000 [00:12<00:00, 1551.15it/s]
--- Performing PCA on Parameter Trajectories ---
Standard NN:
PINN:
--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for Standard NN ---
Evaluating Loss Landscape [Standard NN]: 100%|██████████| 50/50 [00:00<00:00, 155.67it/s]
--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for PINN ---
Evaluating Loss Landscape [PINN]: 100%|██████████| 50/50 [00:00<00:00, 74.14it/s]
--- Evaluating Lipschitz Constants ---
Standard NN Lipschitz Constant: 4.6182
PINN Lipschitz Constant: 14.7301
--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for Standard NN ---
Estimating Rademacher Complexity: 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 50165.10it/s]
Standard NN Rademacher Complexity: 0.0028
--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for PINN ---
Estimating Rademacher Complexity: 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 55036.14it/s]
PINN Rademacher Complexity: 0.0064
=== Network Size: 16 ===
--- Training Standard Neural Network ---
Training Standard NN: 100%|██████████| 1000/1000 [00:00<00:00, 1706.00it/s]
--- Training Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN) ---
Training PINN: 100%|██████████| 20000/20000 [00:14<00:00, 1388.09it/s]
--- Performing PCA on Parameter Trajectories ---
Standard NN:
PINN:
--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for Standard NN ---
Evaluating Loss Landscape [Standard NN]: 100%|██████████| 50/50 [00:00<00:00, 153.87it/s]
--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for PINN ---
Evaluating Loss Landscape [PINN]: 100%|██████████| 50/50 [00:00<00:00, 66.45it/s]
--- Evaluating Lipschitz Constants ---
Standard NN Lipschitz Constant: 17.2926
PINN Lipschitz Constant: 17.0874
--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for Standard NN ---
Estimating Rademacher Complexity: 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 50994.58it/s]
Standard NN Rademacher Complexity: 0.0099
--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for PINN ---
Estimating Rademacher Complexity: 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 52824.99it/s]
PINN Rademacher Complexity: 0.0090
=== Network Size: 32 ===
--- Training Standard Neural Network ---
Training Standard NN: 100%|██████████| 1000/1000 [00:00<00:00, 2121.37it/s]
--- Training Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN) ---
Training PINN: 100%|██████████| 20000/20000 [00:14<00:00, 1375.68it/s]
--- Performing PCA on Parameter Trajectories ---
Standard NN:
PINN:
--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for Standard NN ---
Evaluating Loss Landscape [Standard NN]: 100%|██████████| 50/50 [00:00<00:00, 142.85it/s]
--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for PINN ---
Evaluating Loss Landscape [PINN]: 100%|██████████| 50/50 [00:00<00:00, 64.38it/s]
--- Evaluating Lipschitz Constants ---
Standard NN Lipschitz Constant: 16.6128
PINN Lipschitz Constant: 17.0423
--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for Standard NN ---
Estimating Rademacher Complexity: 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 46187.69it/s]
Standard NN Rademacher Complexity: 0.0123
--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for PINN ---
Estimating Rademacher Complexity: 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 52441.91it/s]
PINN Rademacher Complexity: 0.0099
=== Network Size: 64 ===
--- Training Standard Neural Network ---
Training Standard NN: 100%|██████████| 1000/1000 [00:00<00:00, 1940.90it/s]
--- Training Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN) ---
Training PINN: 100%|██████████| 20000/20000 [00:16<00:00, 1232.25it/s]
--- Performing PCA on Parameter Trajectories ---
Standard NN:
PINN:
--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for Standard NN ---
Evaluating Loss Landscape [Standard NN]: 100%|██████████| 50/50 [00:00<00:00, 127.94it/s]
--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for PINN ---
Evaluating Loss Landscape [PINN]: 100%|██████████| 50/50 [00:00<00:00, 57.94it/s]
--- Evaluating Lipschitz Constants ---
Standard NN Lipschitz Constant: 17.9082
PINN Lipschitz Constant: 17.1785
--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for Standard NN ---
Estimating Rademacher Complexity: 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 52064.35it/s]
Standard NN Rademacher Complexity: 0.0180
--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for PINN ---
Estimating Rademacher Complexity: 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 59417.82it/s]
PINN Rademacher Complexity: 0.0081
=== Network Size: 128 ===
--- Training Standard Neural Network ---
Training Standard NN: 100%|██████████| 1000/1000 [00:00<00:00, 1729.41it/s]
--- Training Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN) ---
Training PINN: 100%|██████████| 20000/20000 [00:19<00:00, 1038.62it/s]
--- Performing PCA on Parameter Trajectories ---
Standard NN:
PINN:
--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for Standard NN ---
Evaluating Loss Landscape [Standard NN]: 100%|██████████| 50/50 [00:00<00:00, 97.24it/s]
--- Evaluating Loss Landscape for PINN ---
Evaluating Loss Landscape [PINN]: 100%|██████████| 50/50 [00:01<00:00, 41.16it/s]
--- Evaluating Lipschitz Constants ---
Standard NN Lipschitz Constant: 17.9274
PINN Lipschitz Constant: 17.1951
--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for Standard NN ---
Estimating Rademacher Complexity: 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 49090.64it/s]
Standard NN Rademacher Complexity: 0.0148
--- Estimating Rademacher Complexity for PINN ---
Estimating Rademacher Complexity: 100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 48993.16it/s]
PINN Rademacher Complexity: 0.0088

import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tqdm import tqdm
class HarmonicOscillator:
def __init__(self, damping_coefficient, natural_frequency):
self.d = damping_coefficient
self.w0 = natural_frequency
assert self.d < self.w0, "Damping coefficient must be less than natural frequency for underdamped oscillator"
self.w = np.sqrt(self.w0**2 - self.d**2)
self.phi = np.arctan(-self.d / self.w)
self.A = 1 / (2 * np.cos(self.phi))
def analytical_solution(self, t):
"""Analytical solution to the 1D underdamped harmonic oscillator problem."""
cos_part = np.cos(self.phi + self.w * t)
exp_part = np.exp(-self.d * t)
u = exp_part * 2 * self.A * cos_part
return u
def generate_data(self, noise_level=0.0):
"""Generates training data for the oscillator with optional noise."""
t = np.linspace(0, 1, 500).reshape(-1, 1)
u = self.analytical_solution(t).reshape(-1, 1)
t_data = t[0:200:20]
u_data = u[0:200:20]
# Add noise to the data
noise = noise_level * np.random.randn(*u_data.shape)
u_data_noisy = u_data + noise
return t, u, t_data, u_data_noisy
def calculate_errors(u_pred, u_exact):
"""
Calculate multiple error metrics between predicted and exact solutions.
Args:
u_pred: Predicted solution values
u_exact: Exact solution values
Returns:
mse: Mean squared error
l2_error: L2 (root mean square) error
max_error: Maximum absolute error
"""
mse = np.mean((u_pred - u_exact)**2)
l2_error = np.sqrt(mse) # Root mean square error
max_error = np.max(np.abs(u_pred - u_exact))
return mse, l2_error, max_error
class NeuralNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layer_sizes):
super(NeuralNetwork, self).__init__()
layers = []
for in_size, out_size in zip(layer_sizes[:-1], layer_sizes[1:]):
layers.append(nn.Linear(in_size, out_size))
layers.append(nn.Tanh())
layers.pop() # Remove the last activation function
self.model = nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
return self.model(x)
def pinn_loss(model, t_data, u_data, t_physics, mu, k):
"""Computes the loss for PINN, including data and physics losses."""
# Data loss
u_pred = model(t_data)
loss_data = nn.MSELoss()(u_pred, u_data)
# Physics loss
t_physics = t_physics.clone().detach().requires_grad_(True)
u_physics = model(t_physics)
du_dt = torch.autograd.grad(u_physics, t_physics, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(u_physics),
create_graph=True)[0]
d2u_dt2 = torch.autograd.grad(du_dt, t_physics, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(du_dt),
create_graph=True)[0]
physics = d2u_dt2 + mu * du_dt + k * u_physics
loss_physics = 1e-4 * torch.mean(physics ** 2)
return loss_data + loss_physics
def train_standard_nn(ho, noise_level=0.0, num_steps=1000):
"""Trains a standard neural network and performs error analysis."""
t, u_exact, t_data, u_data = ho.generate_data(noise_level=noise_level)
# Initialize neural network model
layer_sizes = [1, 32, 32, 32, 1]
model = NeuralNetwork(layer_sizes)
model.train()
# Prepare data
t_data_tensor = torch.tensor(t_data, dtype=torch.float32)
u_data_tensor = torch.tensor(u_data, dtype=torch.float32)
t_full_tensor = torch.tensor(t, dtype=torch.float32)
# Define optimizer and loss function
learning_rate = 1e-3
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
# Training loop
for step in range(num_steps):
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
u_pred = model(t_data_tensor)
loss = criterion(u_pred, u_data_tensor)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Evaluate model
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
u_pred_full = model(t_full_tensor).numpy()
# Calculate all error metrics
mse, l2_error, max_error = calculate_errors(u_pred_full, u_exact)
return mse, l2_error, max_error, u_pred_full, t, u_exact, t_data, u_data
def train_pinn(ho, noise_level=0.0, num_steps=20000):
"""Trains a physics-informed neural network and performs error analysis."""
t, u_exact, t_data, u_data = ho.generate_data(noise_level=noise_level)
# Physics points for PINN
t_physics = np.linspace(0, 1, 30).reshape(-1, 1)
mu = 2 * ho.d
k_param = ho.w0**2
# Initialize neural network model
layer_sizes = [1, 64, 64, 64, 1]
model = NeuralNetwork(layer_sizes)
model.train()
# Prepare data
t_data_tensor = torch.tensor(t_data, dtype=torch.float32)
u_data_tensor = torch.tensor(u_data, dtype=torch.float32)
t_full_tensor = torch.tensor(t, dtype=torch.float32)
t_physics_tensor = torch.tensor(t_physics, dtype=torch.float32)
mu_tensor = torch.tensor(mu, dtype=torch.float32)
k_param_tensor = torch.tensor(k_param, dtype=torch.float32)
# Define optimizer
learning_rate = 1e-4
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
for step in range(num_steps):
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = pinn_loss(model, t_data_tensor, u_data_tensor, t_physics_tensor, mu_tensor, k_param_tensor)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Evaluate model
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
u_pred_full = model(t_full_tensor).numpy()
# Calculate all error metrics
mse, l2_error, max_error = calculate_errors(u_pred_full, u_exact)
return mse, l2_error, max_error, u_pred_full, t, u_exact, t_data, u_data
def stability_analysis():
# Initialize harmonic oscillator
ho = HarmonicOscillator(damping_coefficient=2, natural_frequency=20)
noise_levels = np.arange(0, 0.11, 0.01) # Noise levels from 0% to 10%
# Initialize arrays for all error metrics
errors_standard_nn = {'mse': [], 'l2': [], 'max': []}
errors_pinn = {'mse': [], 'l2': [], 'max': []}
for noise_level in noise_levels:
print(f"Training models with noise level: {noise_level*100:.0f}%")
# Train standard neural network
mse_nn, l2_nn, max_nn, u_pred_nn, t_nn, u_exact_nn, t_data_nn, u_data_nn = train_standard_nn(
ho, noise_level=noise_level, num_steps=2000)
errors_standard_nn['mse'].append(mse_nn)
errors_standard_nn['l2'].append(l2_nn)
errors_standard_nn['max'].append(max_nn)
# Train PINN
mse_pinn, l2_pinn, max_pinn, u_pred_pinn, t_pinn, u_exact_pinn, t_data_pinn, u_data_pinn = train_pinn(
ho, noise_level=noise_level, num_steps=20000)
errors_pinn['mse'].append(mse_pinn)
errors_pinn['l2'].append(l2_pinn)
errors_pinn['max'].append(max_pinn)
print(f"Standard NN - MSE: {mse_nn:.6f}, L2: {l2_nn:.6f}, Max: {max_nn:.6f}")
print(f"PINN - MSE: {mse_pinn:.6f}, L2: {l2_pinn:.6f}, Max: {max_pinn:.6f}")
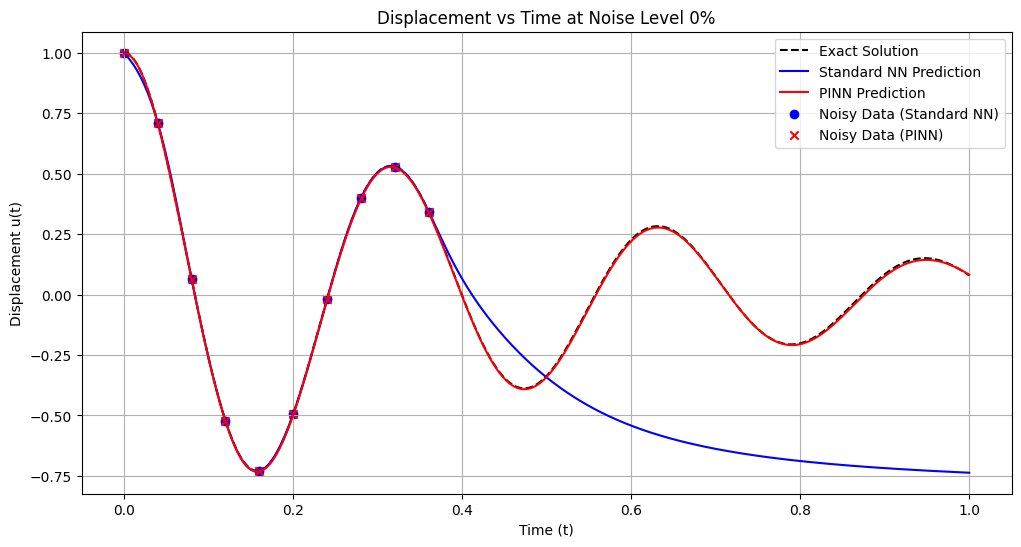
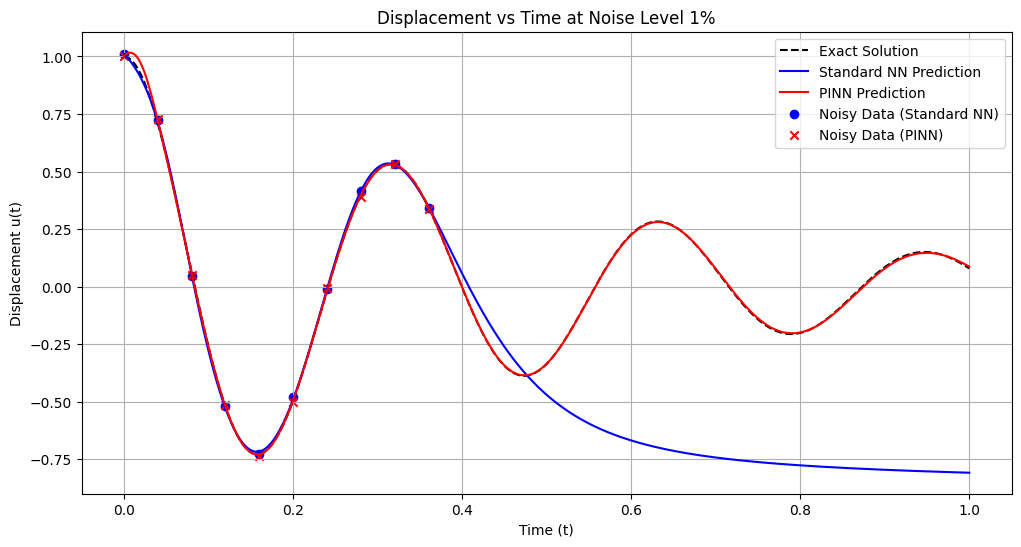
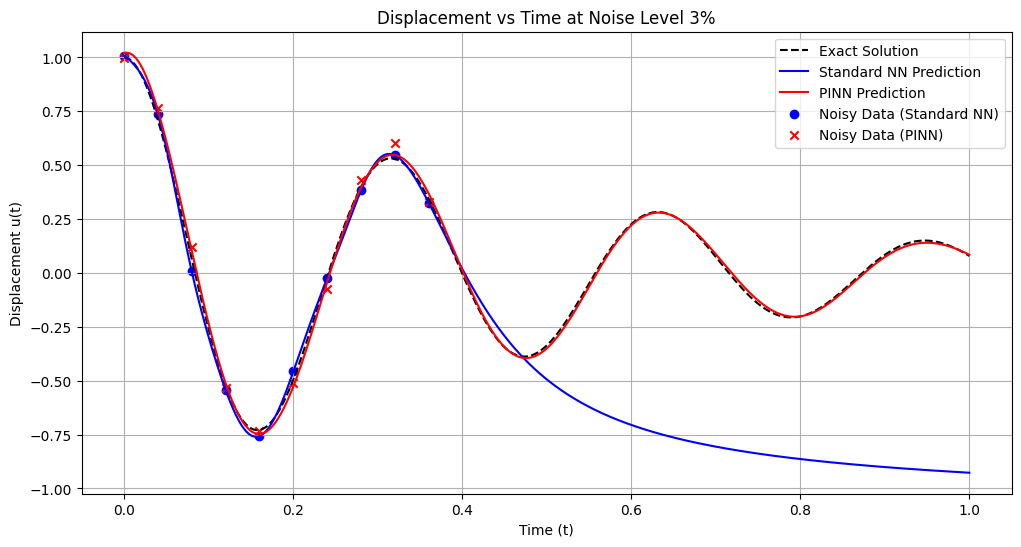
# Plotting the final position vs time estimates
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(t_nn, u_exact_nn, 'k--', label='Exact Solution')
plt.plot(t_nn, u_pred_nn, 'b-', label='Standard NN Prediction')
plt.plot(t_pinn, u_pred_pinn, 'r-', label='PINN Prediction')
plt.scatter(t_data_nn, u_data_nn, color='blue', marker='o', label='Noisy Data (Standard NN)')
plt.scatter(t_data_pinn, u_data_pinn, color='red', marker='x', label='Noisy Data (PINN)')
plt.title(f'Displacement vs Time at Noise Level {noise_level*100:.0f}%')
plt.xlabel('Time (t)')
plt.ylabel('Displacement u(t)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
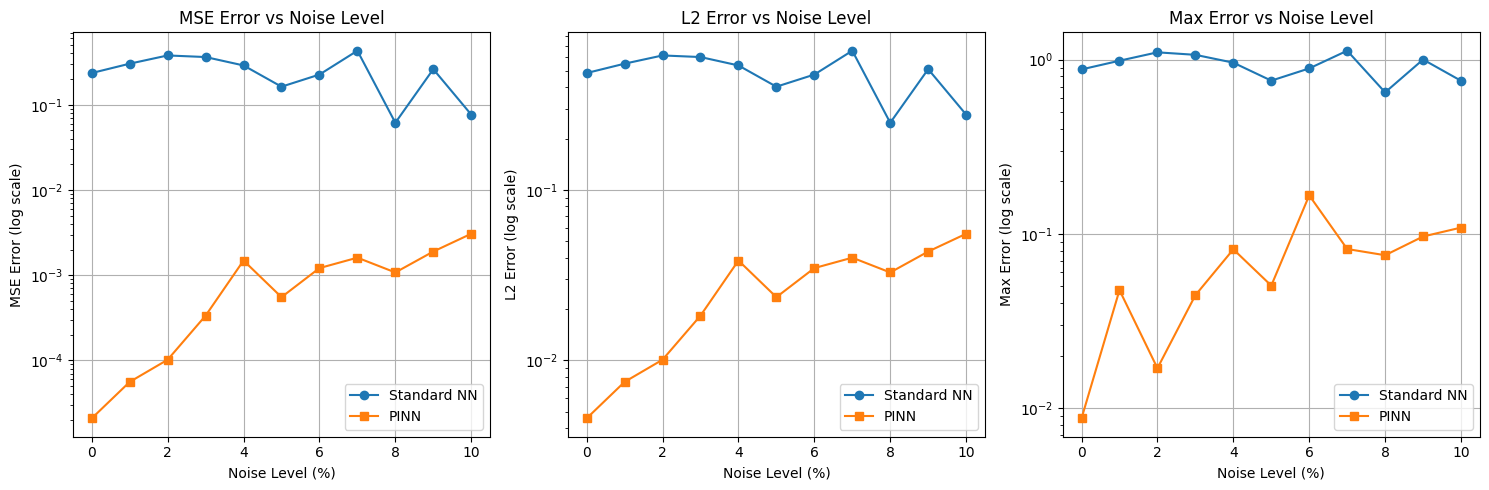
# Create subplots for different error metrics
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 5))
metrics = ['MSE', 'L2', 'Max']
error_keys = ['mse', 'l2', 'max']
for ax, metric, key in zip(axes, metrics, error_keys):
ax.plot(noise_levels * 100, errors_standard_nn[key], 'o-', label='Standard NN')
ax.plot(noise_levels * 100, errors_pinn[key], 's-', label='PINN')
ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.set_xlabel('Noise Level (%)')
ax.set_ylabel(f'{metric} Error (log scale)')
ax.set_title(f'{metric} Error vs Noise Level')
ax.legend()
ax.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
stability_analysis()
Training models with noise level: 0%
Standard NN - MSE: 0.235532, L2: 0.485317, Max: 0.878342
PINN - MSE: 0.000021, L2: 0.004572, Max: 0.008715
Training models with noise level: 1%
Standard NN - MSE: 0.303261, L2: 0.550692, Max: 0.985226
PINN - MSE: 0.000056, L2: 0.007481, Max: 0.047476
Training models with noise level: 2%
Standard NN - MSE: 0.378806, L2: 0.615472, Max: 1.100795
PINN - MSE: 0.000102, L2: 0.010094, Max: 0.016907

Training models with noise level: 3%
Standard NN - MSE: 0.362813, L2: 0.602340, Max: 1.065039
PINN - MSE: 0.000335, L2: 0.018306, Max: 0.044401
Training models with noise level: 4%
Standard NN - MSE: 0.289148, L2: 0.537725, Max: 0.960132
PINN - MSE: 0.001486, L2: 0.038548, Max: 0.081409
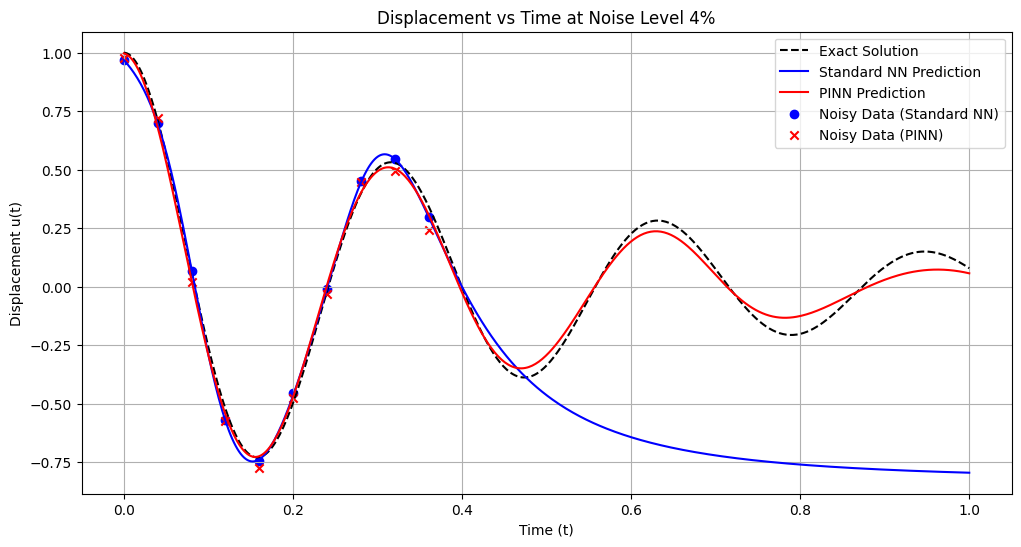
Training models with noise level: 5%
Standard NN - MSE: 0.162859, L2: 0.403558, Max: 0.757030
PINN - MSE: 0.000552, L2: 0.023504, Max: 0.050388
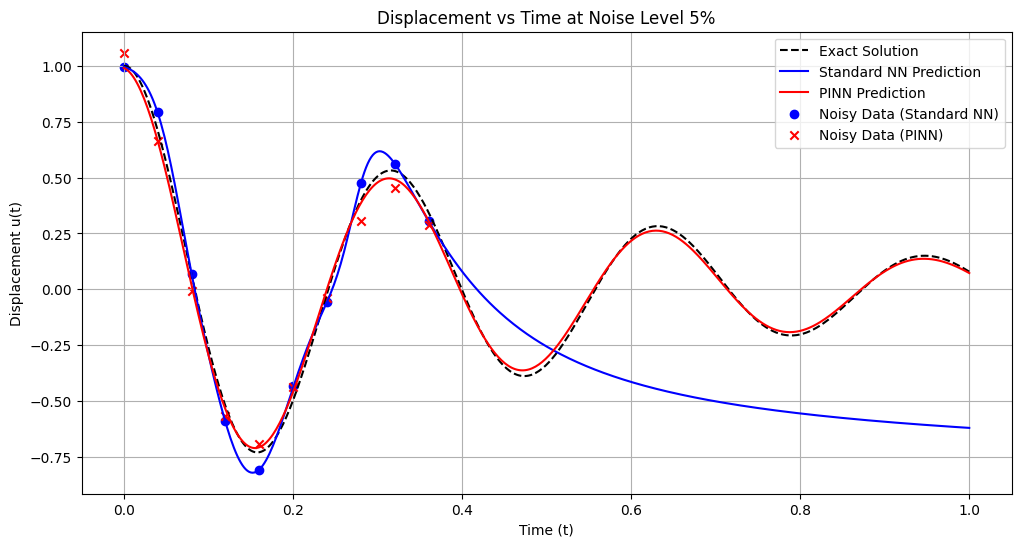
Training models with noise level: 6%
Standard NN - MSE: 0.225999, L2: 0.475393, Max: 0.890008
PINN - MSE: 0.001211, L2: 0.034802, Max: 0.166145
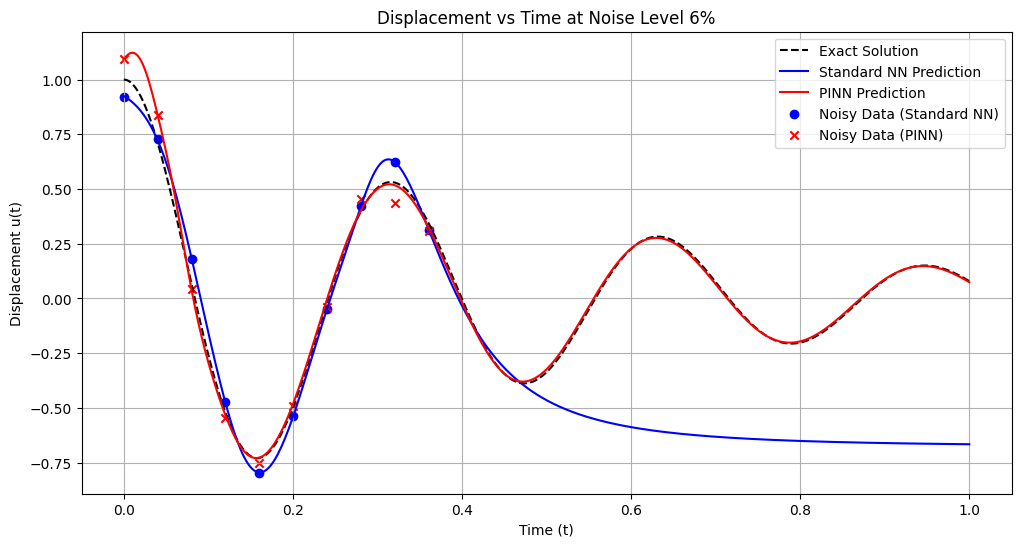
Training models with noise level: 7%
Standard NN - MSE: 0.430483, L2: 0.656112, Max: 1.124572
PINN - MSE: 0.001606, L2: 0.040072, Max: 0.081739

Training models with noise level: 8%
Standard NN - MSE: 0.061464, L2: 0.247919, Max: 0.648373
PINN - MSE: 0.001076, L2: 0.032808, Max: 0.075289

Training models with noise level: 9%
Standard NN - MSE: 0.261475, L2: 0.511347, Max: 1.000848
PINN - MSE: 0.001894, L2: 0.043521, Max: 0.096451

Training models with noise level: 10%
Standard NN - MSE: 0.076645, L2: 0.276848, Max: 0.755745
PINN - MSE: 0.003063, L2: 0.055346, Max: 0.108503
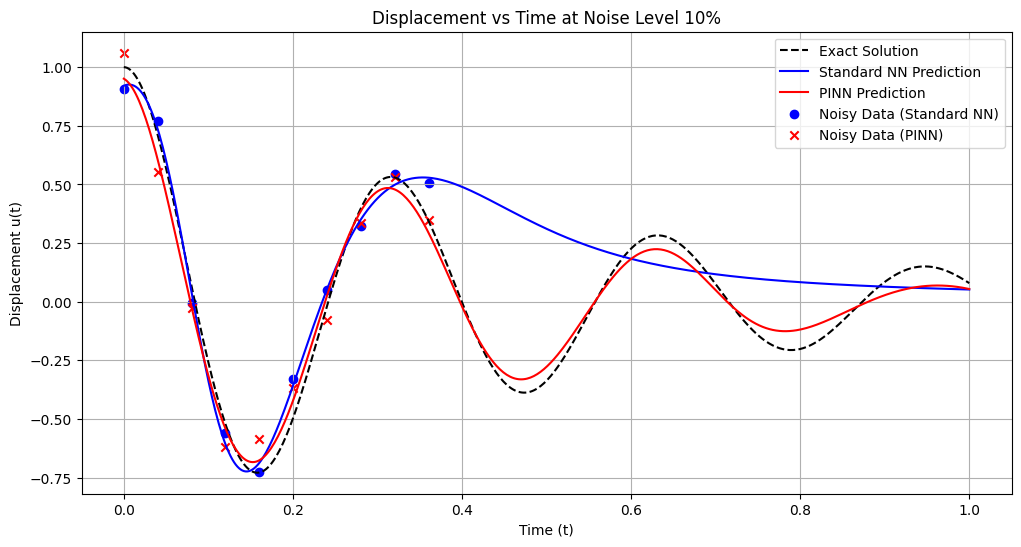
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tqdm import tqdm
# Set random seeds for reproducibility
np.random.seed(42)
torch.manual_seed(42)
class HarmonicOscillator:
def __init__(self, damping_coefficient, natural_frequency):
self.d = damping_coefficient
self.w0 = natural_frequency
assert self.d < self.w0, "Damping coefficient must be less than natural frequency for underdamped oscillator"
self.w = np.sqrt(self.w0**2 - self.d**2)
self.phi = np.arctan(-self.d / self.w)
self.A = 1 / (2 * np.cos(self.phi))
def analytical_solution(self, t):
"""Analytical solution to the 1D underdamped harmonic oscillator problem."""
cos_part = np.cos(self.phi + self.w * t)
exp_part = np.exp(-self.d * t)
u = exp_part * 2 * self.A * cos_part
return u
def generate_data(self, noise_level=0.0):
"""Generates training data for the oscillator with optional noise."""
t = np.linspace(0, 1, 500).reshape(-1, 1)
u = self.analytical_solution(t).reshape(-1, 1)
t_data = t[0:200:20]
u_data = u[0:200:20]
# Add noise to the data
noise = noise_level * np.random.randn(*u_data.shape)
u_data_noisy = u_data + noise
return t, u, t_data, u_data_noisy
class NeuralNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layer_sizes):
super(NeuralNetwork, self).__init__()
layers = []
for in_size, out_size in zip(layer_sizes[:-1], layer_sizes[1:]):
layers.append(nn.Linear(in_size, out_size))
layers.append(nn.Tanh())
layers.pop() # Remove the last activation function
self.model = nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
return self.model(x)
def pinn_loss(model, t_data, u_data, t_physics, mu, k):
"""Computes the loss for PINN, including data and physics losses."""
# Data loss
u_pred = model(t_data)
loss_data = nn.MSELoss()(u_pred, u_data)
# Physics loss
t_physics = t_physics.clone().detach().requires_grad_(True)
u_physics = model(t_physics)
du_dt = torch.autograd.grad(u_physics, t_physics, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(u_physics),
create_graph=True)[0]
d2u_dt2 = torch.autograd.grad(du_dt, t_physics, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(du_dt),
create_graph=True)[0]
physics = d2u_dt2 + mu * du_dt + k * u_physics
loss_physics = 1e-4 * torch.mean(physics ** 2)
return loss_data + loss_physics
def train_standard_nn(ho, num_steps=10000):
"""Trains a standard neural network on clean data."""
t, u_exact, t_data, u_data = ho.generate_data(noise_level=0.0)
# Initialize neural network model
layer_sizes = [1, 64, 64, 64, 1] # Updated to 64 neurons per layer
model = NeuralNetwork(layer_sizes)
model.train()
# Prepare data
t_data_tensor = torch.tensor(t_data, dtype=torch.float32)
u_data_tensor = torch.tensor(u_data, dtype=torch.float32)
t_full_tensor = torch.tensor(t, dtype=torch.float32)
# Define optimizer and loss function
learning_rate = 1e-3
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
# Training loop
for step in tqdm(range(num_steps), desc="Training Standard NN"):
optimizer.zero_grad()
u_pred = model(t_data_tensor)
loss = criterion(u_pred, u_data_tensor)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Evaluate model
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
u_pred_full = model(t_full_tensor).numpy()
# Calculate error metrics
error = np.mean((u_pred_full - u_exact)**2)
return model, error, u_pred_full, t, u_exact
def train_pinn(ho, num_steps=20000):
"""Trains a physics-informed neural network on clean data."""
t, u_exact, t_data, u_data = ho.generate_data(noise_level=0.0)
# Physics points for PINN
t_physics = np.linspace(0, 1, 100).reshape(-1, 1) # Increased physics points for better training
mu = 2 * ho.d
k_param = ho.w0**2
# Initialize neural network model
layer_sizes = [1, 64, 64, 64, 1] # Updated to 64 neurons per layer
model = NeuralNetwork(layer_sizes)
model.train()
# Prepare data
t_data_tensor = torch.tensor(t_data, dtype=torch.float32)
u_data_tensor = torch.tensor(u_data, dtype=torch.float32)
t_physics_tensor = torch.tensor(t_physics, dtype=torch.float32)
mu_tensor = torch.tensor(mu, dtype=torch.float32)
k_param_tensor = torch.tensor(k_param, dtype=torch.float32)
# Define optimizer
learning_rate = 1e-4
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# Training loop
for step in tqdm(range(num_steps), desc="Training PINN"):
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = pinn_loss(model, t_data_tensor, u_data_tensor, t_physics_tensor, mu_tensor, k_param_tensor)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Evaluate model
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
u_pred_full = model(torch.tensor(t, dtype=torch.float32)).numpy()
# Calculate error metrics
error = np.mean((u_pred_full - u_exact)**2)
return model, error, u_pred_full, t, u_exact
def compute_beta(model, t, u_exact, noise_level, device='cpu'):
"""
Computes the stability constant beta for a given model and noise level.
Args:
model: Trained neural network model.
t: Original time points (numpy array).
u_exact: Exact solution at time points t (numpy array).
noise_level: Standard deviation of Gaussian noise to add to t.
device: Device to perform computations on.
Returns:
beta: Stability constant.
"""
# Convert t to torch tensor
t_tensor = torch.tensor(t, dtype=torch.float32).to(device)
t_tensor.requires_grad = False
# Generate Gaussian noise
epsilon = noise_level * np.random.randn(*t.shape).astype(np.float32)
epsilon_tensor = torch.tensor(epsilon).to(device)
# Perturbed inputs
t_noisy_tensor = t_tensor + epsilon_tensor
# Compute model outputs
with torch.no_grad():
f_t = model(t_tensor).cpu().numpy()
f_t_noisy = model(t_noisy_tensor).cpu().numpy()
# Compute norms
numerator = np.linalg.norm(f_t_noisy - f_t)
denominator = np.linalg.norm(epsilon)
# Handle division by zero or very small denominator
if denominator < 1e-8:
beta = np.nan # Undefined
else:
beta = numerator / denominator
return beta
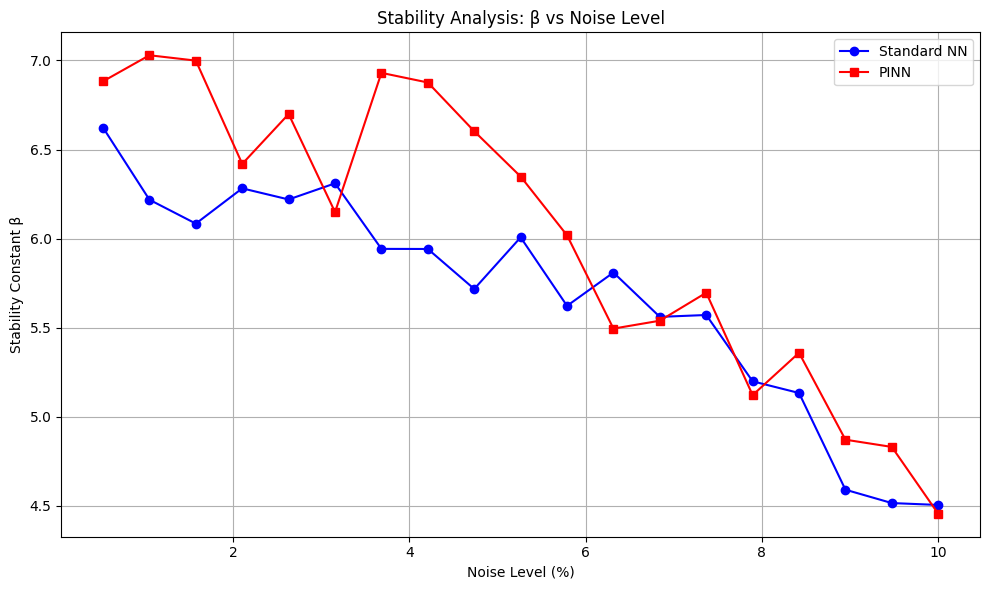
def stability_analysis():
# Initialize harmonic oscillator
ho = HarmonicOscillator(damping_coefficient=2, natural_frequency=20)
# Train models on clean data
print("Training Standard NN...")
model_nn, error_nn, u_pred_nn, t_nn, u_exact_nn = train_standard_nn(ho, num_steps=10000)
print(f"Standard NN Training Error: {error_nn:.6f}")
print("Training PINN...")
model_pinn, error_pinn, u_pred_pinn, t_pinn, u_exact_pinn = train_pinn(ho, num_steps=20000)
print(f"PINN Training Error: {error_pinn:.6f}")
# Define noise levels (standard deviation of Gaussian noise)
noise_levels = np.linspace(0, 0.1, 20) # Noise levels from 0% to 10%
beta_standard_nn = []
beta_pinn = []
for sigma in tqdm(noise_levels, desc="Computing Beta"):
beta_nn = compute_beta(model_nn, t_nn, u_exact_nn, noise_level=sigma)
beta_pinn_val = compute_beta(model_pinn, t_pinn, u_exact_pinn, noise_level=sigma)
beta_standard_nn.append(beta_nn)
beta_pinn.append(beta_pinn_val)
# Convert noise levels to percentages for plotting
noise_percentages = noise_levels * 100
# Convert beta lists to numpy arrays for easier handling
beta_standard_nn = np.array(beta_standard_nn)
beta_pinn = np.array(beta_pinn)
# Handle any NaN values by setting them to zero or another appropriate value
# Here, we'll exclude them from the plot
valid_indices_nn = ~np.isnan(beta_standard_nn)
valid_indices_pinn = ~np.isnan(beta_pinn)
# Plotting Beta vs Noise Level
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(noise_percentages[valid_indices_nn], beta_standard_nn[valid_indices_nn],
'o-', label='Standard NN', color='blue')
plt.plot(noise_percentages[valid_indices_pinn], beta_pinn[valid_indices_pinn],
's-', label='PINN', color='red')
plt.xlabel('Noise Level (%)')
plt.ylabel('Stability Constant β')
plt.title('Stability Analysis: β vs Noise Level')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
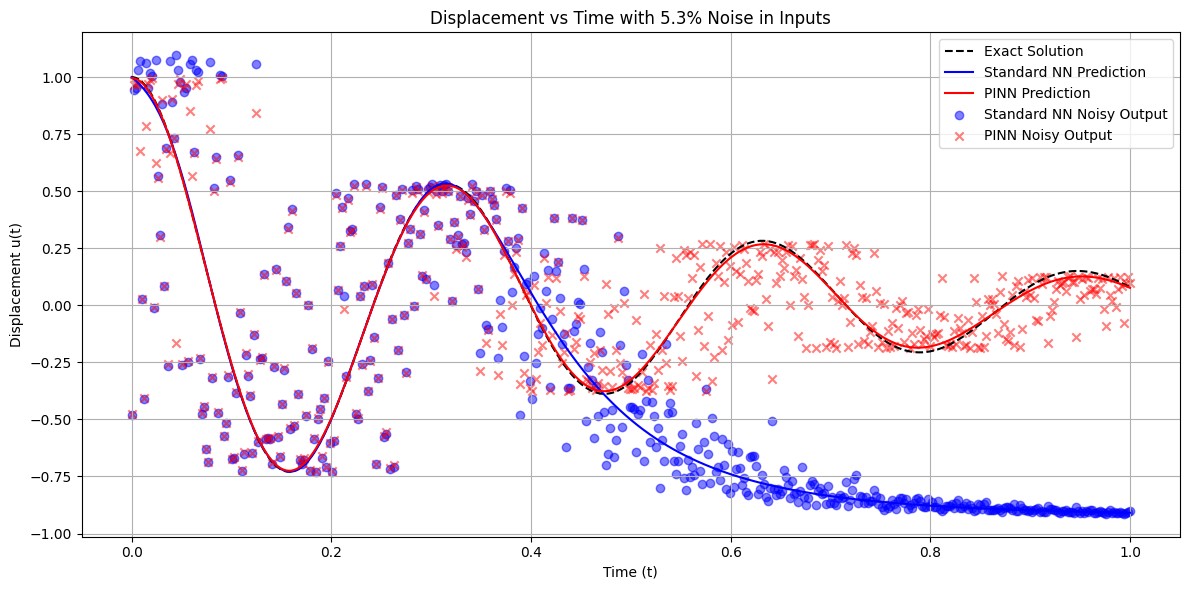
# Plotting the predictions vs exact solution for a representative noise level
representative_noise = 0.05 # 5%
idx = np.argmin(np.abs(noise_levels - representative_noise))
sigma = noise_levels[idx]
print(f"\nRepresentative Noise Level: {sigma*100:.1f}%")
# Generate noisy inputs
epsilon = sigma * np.random.randn(*t_nn.shape).astype(np.float32)
t_noisy = t_nn + epsilon
t_noisy_tensor = torch.tensor(t_noisy, dtype=torch.float32)
# Get model predictions
with torch.no_grad():
u_pred_nn_noisy = model_nn(torch.tensor(t_noisy, dtype=torch.float32)).cpu().numpy()
u_pred_pinn_noisy = model_pinn(torch.tensor(t_noisy, dtype=torch.float32)).cpu().numpy()
# Plotting
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(t_nn, u_exact_nn, 'k--', label='Exact Solution')
plt.plot(t_nn, u_pred_nn, 'b-', label='Standard NN Prediction')
plt.plot(t_nn, u_pred_pinn, 'r-', label='PINN Prediction')
plt.scatter(t_nn, u_pred_nn_noisy, color='blue', marker='o', label='Standard NN Noisy Output', alpha=0.5)
plt.scatter(t_nn, u_pred_pinn_noisy, color='red', marker='x', label='PINN Noisy Output', alpha=0.5)
plt.title(f'Displacement vs Time with {sigma*100:.1f}% Noise in Inputs')
plt.xlabel('Time (t)')
plt.ylabel('Displacement u(t)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
stability_analysis()
def compute_local_beta(model, t, u_exact, noise_level, window_size=0.1):
"""
Computes stability constant β locally across different time windows.
Args:
model: Trained neural network model
t: Time points array
u_exact: Exact solution
noise_level: Noise level for perturbation
window_size: Size of time window for local analysis
Returns:
local_betas: Array of local stability constants
window_centers: Centers of time windows
"""
local_betas = []
window_centers = []
# Sliding window analysis
for t_center in np.arange(0, 1-window_size/2, window_size/2):
# Define window bounds
t_min = t_center
t_max = t_center + window_size
# Get indices for current window
mask = (t.flatten() >= t_min) & (t.flatten() <= t_max)
t_window = t[mask]
if len(t_window) < 2: # Skip if window too small
continue
# Add noise to window
t_window_tensor = torch.tensor(t_window, dtype=torch.float32).reshape(-1, 1)
epsilon = noise_level * np.random.randn(*t_window.shape).astype(np.float32)
t_noisy_tensor = t_window_tensor + torch.tensor(epsilon).reshape(-1, 1)
# Compute predictions
with torch.no_grad():
u_pred = model(t_window_tensor)
u_pred_noisy = model(t_noisy_tensor)
# Compute local beta
numerator = torch.norm(u_pred_noisy - u_pred).item()
denominator = np.linalg.norm(epsilon)
if denominator > 1e-8:
local_beta = numerator / denominator
local_betas.append(local_beta)
window_centers.append(t_center + window_size/2)
return np.array(local_betas), np.array(window_centers)
def analyze_stability_with_exact_solution():
# Initialize harmonic oscillator
ho = HarmonicOscillator(damping_coefficient=2, natural_frequency=20)
# Train both models
model_nn, _, _, t, u_exact = train_standard_nn(ho)
model_pinn, _, _, _, _ = train_pinn(ho)
# Define noise levels
noise_levels = [0.01, 0.05, 0.1] # 1%, 5%, and 10% noise
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
for i, noise_level in enumerate(noise_levels):
# Compute local stability for both models
beta_nn, centers_nn = compute_local_beta(model_nn, t, u_exact, noise_level)
beta_pinn, centers_pinn = compute_local_beta(model_pinn, t, u_exact, noise_level)
# Plot local stability
plt.subplot(2, len(noise_levels), i+1)
plt.plot(centers_nn, beta_nn, 'b-', label='Standard NN')
plt.plot(centers_pinn, beta_pinn, 'r-', label='PINN')
plt.title(f'Local Stability (β) at {noise_level*100}% Noise')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Local β')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
# Plot relative error against exact solution
plt.subplot(2, len(noise_levels), i+len(noise_levels)+1)
# Add noise to full time domain
t_tensor = torch.tensor(t, dtype=torch.float32)
epsilon = noise_level * np.random.randn(*t.shape).astype(np.float32)
t_noisy = t_tensor + torch.tensor(epsilon)
# Compute predictions
with torch.no_grad():
u_nn = model_nn(t_noisy).numpy()
u_pinn = model_pinn(t_noisy).numpy()
# Plot relative errors
rel_error_nn = np.abs(u_nn - u_exact) / np.abs(u_exact)
rel_error_pinn = np.abs(u_pinn - u_exact) / np.abs(u_exact)
plt.plot(t, rel_error_nn, 'b-', label='Standard NN')
plt.plot(t, rel_error_pinn, 'r-', label='PINN')
plt.title(f'Relative Error at {noise_level*100}% Noise')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Relative Error')
plt.yscale('log')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Print summary statistics
print("\nStability Analysis Summary:")
for noise_level in noise_levels:
beta_nn, _ = compute_local_beta(model_nn, t, u_exact, noise_level)
beta_pinn, _ = compute_local_beta(model_pinn, t, u_exact, noise_level)
print(f"\nNoise Level: {noise_level*100}%")
print(f"Standard NN - Mean β: {np.mean(beta_nn):.4f}, Max β: {np.max(beta_nn):.4f}")
print(f"PINN - Mean β: {np.mean(beta_pinn):.4f}, Max β: {np.max(beta_pinn):.4f}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
analyze_stability_with_exact_solution()
Training Standard NN...
Training Standard NN: 100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [00:02<00:00, 3634.93it/s]
Standard NN Training Error: 0.375134
Training PINN...
Training PINN: 100%|██████████| 20000/20000 [00:16<00:00, 1184.05it/s]
PINN Training Error: 0.000119
Computing Beta: 100%|██████████| 20/20 [00:00<00:00, 684.93it/s]
Representative Noise Level: 5.3%
Training Standard NN: 100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [00:02<00:00, 3869.62it/s]
Training PINN: 100%|██████████| 20000/20000 [00:16<00:00, 1193.58it/s]
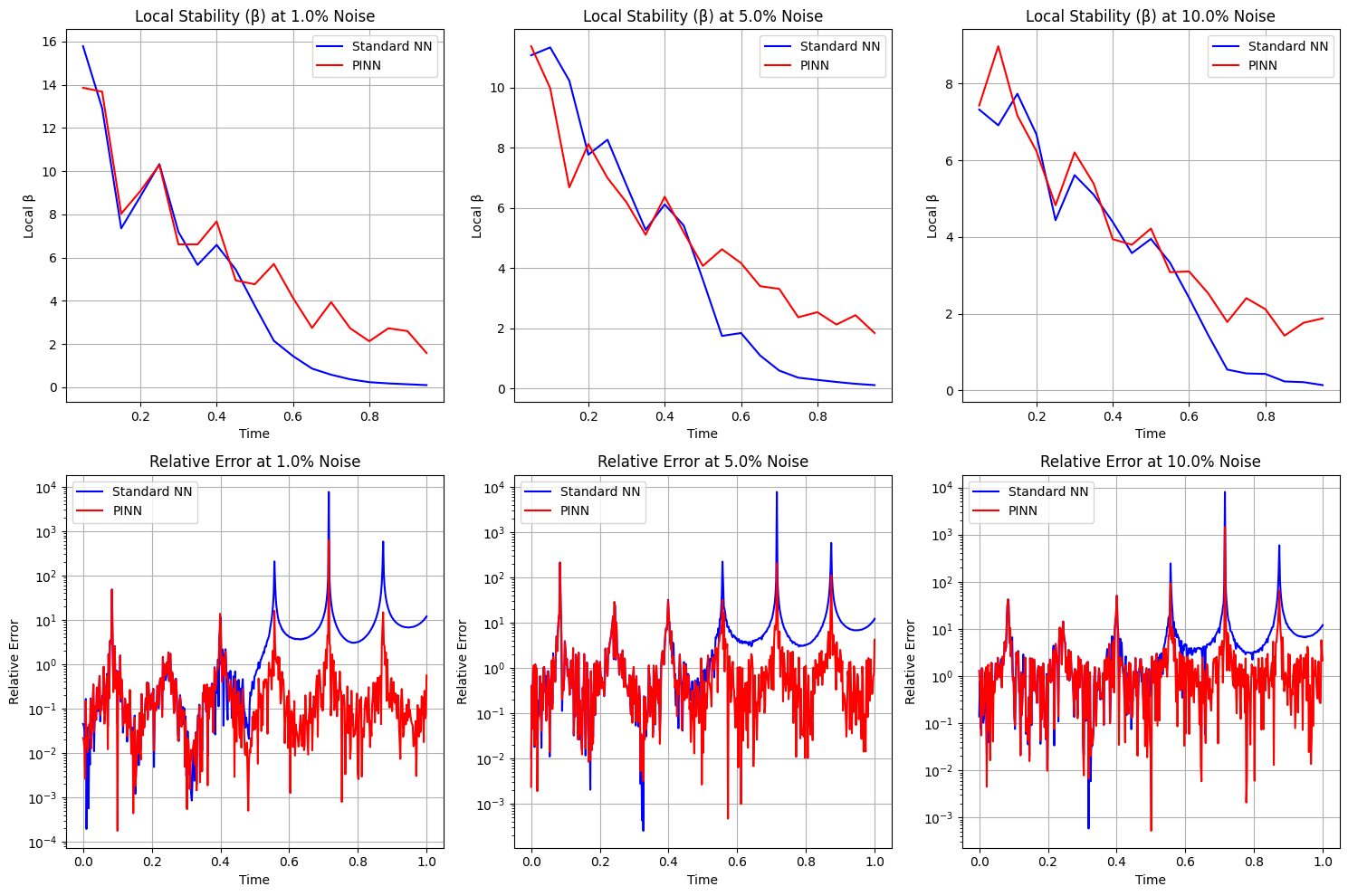
Stability Analysis Summary:
Noise Level: 1.0%
Standard NN - Mean β: 4.6948, Max β: 12.8486
PINN - Mean β: 6.0357, Max β: 13.4400
Noise Level: 5.0%
Standard NN - Mean β: 4.2028, Max β: 12.2113
PINN - Mean β: 5.1577, Max β: 10.9558
Noise Level: 10.0%
Standard NN - Mean β: 3.6617, Max β: 9.7699
PINN - Mean β: 3.9039, Max β: 7.8200
